지능화 파일럿 프로젝트 - UNet으로 이차전지극판 영역분할
- 산업인공지능학과 대학원 2022254026 김홍열
UNet 논문
프로젝트 목표
- UNet 모델을 학습하여 이차전지극판 영상에서 극판부분을 영역분할
특이사항
- Dataset은 기업보안으로 인해 반출 불가
- 조명 밝기 변화를 이미지 별로 저장하였으므로 관련 Argumentation은 제외
- GPU 메모리 한계로 512x512 크기로 리사이즈하여 학습
데이터셋
- 이차전지 업체에서 확보한 샘플을 12M 카메라로, Ring, Bar 조명 변화별 영상 촬영
- Gold, Silver 극판별 각 9개의 모양을 정의 및 마스크 생성
- Argumentation: Normalization(mean=0.5, std=0.5), RandomFlip(), Rotate(angle_range=(-90, 90))
- 이미지 크기: 5120x5120x1
- 학습데이터 수: 13638
- 검증데이터 수: 3896
- 테스트데이터 수: 1949
- 총 데이터 수: 19483
프로젝트 코드
Load Dataset
import os
from glob import glob
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import random
import cv2
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, list_imgs, list_masks, transform=None):
self.list_imgs = list_imgs
self.list_masks = list_masks
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.list_imgs)
def __getitem__(self, index):
img_path = self.list_imgs[index]
mask_path = self.list_masks[index]
img = cv2.imread(img_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
mask = cv2.imread(mask_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 이미지 크기를 512x512로 변경
img = cv2.resize(img, (512, 512), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
mask = cv2.resize(mask, (512, 512), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
mask = mask.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
if img.ndim == 2:
img = img[:, :, np.newaxis]
if mask.ndim == 2:
mask = mask[:, :, np.newaxis]
data = {'input': img, 'label': mask}
if self.transform:
data = self.transform(data)
return data
def create_datasets(img_dir, mask_dir, train_ratio=0.7, val_ratio=0.2, transform=None):
list_imgs = sorted(glob(os.path.join(img_dir, '**', '*.png'), recursive=True))
list_masks = sorted(glob(os.path.join(mask_dir, '**', '*.png'), recursive=True))
combined = list(zip(list_imgs, list_masks))
random.shuffle(combined)
list_imgs, list_masks = zip(*combined)
num_imgs = len(list_imgs)
num_train = int(num_imgs * train_ratio)
num_val = int(num_imgs * val_ratio)
train_set = CustomDataset(list_imgs[:num_train], list_masks[:num_train], transform)
val_set = CustomDataset(list_imgs[num_train:num_train + num_val], list_masks[num_train:num_train + num_val], transform)
test_set = CustomDataset(list_imgs[num_train + num_val:], list_masks[num_train + num_val:], transform)
return train_set, val_set, test_set
Test DatasetLoader
# 사용 예시
dir_img = 'C:/Users/pinb/Desktop/imgs'
dir_mask = 'C:/Users/pinb/Desktop/masks'
train_set, val_set, test_set = create_datasets(dir_img, dir_mask)
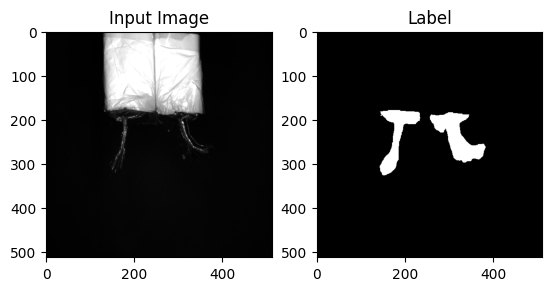
# 첫 번째 이미지 확인 (예: train set)
data = train_set.__getitem__(7777) # 이미지 불러오기
input_img = data['input']
label = data['label']
# 이미지 시각화
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(input_img.reshape(input_img.shape[0], input_img.shape[1]), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(label.reshape(label.shape[0], label.shape[1]), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Label')
plt.show()
Argumentation
# 트렌스폼 구현하기
class ToTensor(object):
# def __call__(self, data):
# label, input = data['label'], data['input']
# label = label.transpose((2, 0, 1)).astype(np.float32)
# input = input.transpose((2, 0, 1)).astype(np.float32)
# data = {'label': torch.from_numpy(label), 'input': torch.from_numpy(input)}
# return data
def __call__(self, data):
label, input = data['label'], data['input']
# 이미지가 이미 그레이스케일이면 채널 차원 추가
if label.ndim == 2:
label = label[:, :, np.newaxis]
if input.ndim == 2:
input = input[:, :, np.newaxis]
# 채널을 첫 번째 차원으로 이동
label = label.transpose((2, 0, 1)).astype(np.float32)
input = input.transpose((2, 0, 1)).astype(np.float32)
data = {'label': torch.from_numpy(label), 'input': torch.from_numpy(input)}
return data
class Normalization(object):
def __init__(self, mean=0.5, std=0.5):
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
def __call__(self, data):
label, input = data['label'], data['input']
input = (input - self.mean) / self.std
data = {'label': label, 'input': input}
return data
class RandomFlip(object):
def __call__(self, data):
label, input = data['label'], data['input']
if np.random.rand() > 0.5:
label = np.fliplr(label)
input = np.fliplr(input)
if np.random.rand() > 0.5:
label = np.flipud(label)
input = np.flipud(input)
data = {'label': label, 'input': input}
return data
# class Resize(object):
# def __init__(self, output_size):
# assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple))
# self.output_size = output_size
# def __call__(self, data):
# label, input = data['label'], data['input']
# h, w = input.shape[:2]
# if isinstance(self.output_size, int):
# if h > w:
# new_h, new_w = self.output_size * h / w, self.output_size
# else:
# new_h, new_w = self.output_size, self.output_size * w / h
# else:
# new_h, new_w = self.output_size
# new_h, new_w = int(new_h), int(new_w)
# input = cv2.resize(input, (new_w, new_h))
# label = cv2.resize(label, (new_w, new_h))
# return {'label': label, 'input': input}
class Rotate(object):
def __init__(self, angle_range):
assert isinstance(angle_range, (tuple, list)) and len(angle_range) == 2
self.angle_min, self.angle_max = angle_range
def __call__(self, data):
label, input = data['label'], data['input']
# NumPy 배열로 변환 (필요한 경우)
if not isinstance(input, np.ndarray):
input = np.array(input)
if not isinstance(label, np.ndarray):
label = np.array(label)
# (H, W, C) 형태를 (H, W)로 변경 (필요한 경우)
if input.ndim == 3 and input.shape[2] == 1:
input = input.squeeze(2)
if label.ndim == 3 and label.shape[2] == 1:
label = label.squeeze(2)
# 랜덤 각도 선택 및 회전 적용
angle = np.random.uniform(self.angle_min, self.angle_max)
h, w = input.shape[:2]
center = (w / 2, h / 2)
rot_matrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)
input = cv2.warpAffine(input, rot_matrix, (w, h))
label = cv2.warpAffine(label, rot_matrix, (w, h))
return {'label': label, 'input': input}
# class Crop(object):
# def __init__(self, output_size):
# assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple))
# if isinstance(output_size, int):
# self.output_size = (output_size, output_size)
# else:
# assert len(output_size) == 2
# self.output_size = output_size
# def __call__(self, data):
# label, input = data['label'], data['input']
# h, w = input.shape[:2]
# new_h, new_w = self.output_size
# top = np.random.randint(0, h - new_h)
# left = np.random.randint(0, w - new_w)
# input = input[top: top + new_h, left: left + new_w]
# label = label[top: top + new_h, left: left + new_w]
# return {'label': label, 'input': input}
Test Argumentation
# 트랜스폼 잘 구현되었는지 확인
transform = transforms.Compose([Normalization(mean=0.5, std=0.5), RandomFlip(), Rotate(angle_range=(-90, 90)), ToTensor()])
dir_img = 'C:/Users/pinb/Desktop/imgs'
dir_mask = 'C:/Users/pinb/Desktop/masks'
train_set, val_set, test_set = create_datasets(img_dir=dir_img, mask_dir=dir_mask, transform=transform)
data = train_set.__getitem__(12599) # 한 이미지 불러오기
input = data['input']
label = data['label']
# 불러온 이미지 시각화
plt.subplot(122)
plt.hist(label.flatten(), bins=20)
plt.title('label')
plt.subplot(121)
plt.hist(input.flatten(), bins=20)
plt.title('input')
# 이미지 시각화
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(input.squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(label.squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Label')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Model Network
## 라이브러리 불러오기
import os
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
## 네트워크 구축하기
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
# Convolution + BatchNormalization + Relu 정의하기
def CBR2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True):
layers = []
layers += [nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding,
bias=bias)]
layers += [nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels)]
layers += [nn.ReLU()]
cbr = nn.Sequential(*layers)
return cbr
# 수축 경로(Contracting path)
self.enc1_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=64)
self.enc1_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.enc2_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128)
self.enc2_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=128)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.enc3_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256)
self.enc3_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256)
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.enc4_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512)
self.enc4_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512)
self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.enc5_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024)
# 확장 경로(Expansive path)
self.dec5_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512)
self.unpool4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512,
kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, bias=True)
self.dec4_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=2 * 512, out_channels=512)
self.dec4_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=256)
self.unpool3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256,
kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, bias=True)
self.dec3_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=2 * 256, out_channels=256)
self.dec3_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128)
self.unpool2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=128,
kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, bias=True)
self.dec2_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=2 * 128, out_channels=128)
self.dec2_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=64)
self.unpool1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64,
kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, bias=True)
self.dec1_2 = CBR2d(in_channels=2 * 64, out_channels=64)
self.dec1_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
# self.enc1_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=64)
# self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# self.enc2_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128)
# self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# self.enc3_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256)
# self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# self.enc4_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512)
# self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# self.enc5_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024)
# # 확장 경로(Expansive path)의 깊이 감소
# self.dec5_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=512)
# self.unpool4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=512, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# self.dec4_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=512 + 512, out_channels=256)
# self.unpool3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# self.dec3_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=256 + 256, out_channels=128)
# self.unpool2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# self.dec2_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=128 + 128, out_channels=64)
# self.unpool1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
# self.dec1_1 = CBR2d(in_channels=64 + 64, out_channels=64)
# self.fc = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
# forward 함수 정의하기
def forward(self, x):
enc1_1 = self.enc1_1(x)
enc1_2 = self.enc1_2(enc1_1)
pool1 = self.pool1(enc1_2)
enc2_1 = self.enc2_1(pool1)
enc2_2 = self.enc2_2(enc2_1)
pool2 = self.pool2(enc2_2)
enc3_1 = self.enc3_1(pool2)
enc3_2 = self.enc3_2(enc3_1)
pool3 = self.pool3(enc3_2)
enc4_1 = self.enc4_1(pool3)
enc4_2 = self.enc4_2(enc4_1)
pool4 = self.pool4(enc4_2)
enc5_1 = self.enc5_1(pool4)
dec5_1 = self.dec5_1(enc5_1)
unpool4 = self.unpool4(dec5_1)
cat4 = torch.cat((unpool4, enc4_2), dim=1)
dec4_2 = self.dec4_2(cat4)
dec4_1 = self.dec4_1(dec4_2)
unpool3 = self.unpool3(dec4_1)
cat3 = torch.cat((unpool3, enc3_2), dim=1)
dec3_2 = self.dec3_2(cat3)
dec3_1 = self.dec3_1(dec3_2)
unpool2 = self.unpool2(dec3_1)
cat2 = torch.cat((unpool2, enc2_2), dim=1)
dec2_2 = self.dec2_2(cat2)
dec2_1 = self.dec2_1(dec2_2)
unpool1 = self.unpool1(dec2_1)
cat1 = torch.cat((unpool1, enc1_2), dim=1)
dec1_2 = self.dec1_2(cat1)
dec1_1 = self.dec1_1(dec1_2)
x = self.fc(dec1_1)
# enc1_1 = self.enc1_1(x)
# pool1 = self.pool1(enc1_1)
# enc2_1 = self.enc2_1(pool1)
# pool2 = self.pool2(enc2_1)
# enc3_1 = self.enc3_1(pool2)
# pool3 = self.pool3(enc3_1)
# enc4_1 = self.enc4_1(pool3)
# pool4 = self.pool4(enc4_1)
# enc5_1 = self.enc5_1(pool4)
# dec5_1 = self.dec5_1(enc5_1)
# unpool4 = self.unpool4(dec5_1)
# cat4 = torch.cat((unpool4, enc4_1), dim=1)
# dec4_1 = self.dec4_1(cat4)
# unpool3 = self.unpool3(dec4_1)
# cat3 = torch.cat((unpool3, enc3_1), dim=1)
# dec3_1 = self.dec3_1(cat3)
# unpool2 = self.unpool2(dec3_1)
# cat2 = torch.cat((unpool2, enc2_1), dim=1)
# dec2_1 = self.dec2_1(cat2)
# unpool1 = self.unpool1(dec2_1)
# cat1 = torch.cat((unpool1, enc1_1), dim=1)
# dec1_1 = self.dec1_1(cat1)
# x = self.fc(dec1_1)
return x
Model Load & Save
## 네트워크 저장하기
def save(ckpt_dir, net, optim, epoch):
if not os.path.exists(ckpt_dir):
os.makedirs(ckpt_dir)
torch.save({'net': net.state_dict(), 'optim': optim.state_dict()},
"%s/model_epoch%d.pth" % (ckpt_dir, epoch))
## 네트워크 불러오기
def load(ckpt_dir, net, optim):
if not os.path.exists(ckpt_dir):
epoch = 0
return net, optim, epoch
ckpt_lst = os.listdir(ckpt_dir)
ckpt_lst.sort(key=lambda f: int(''.join(filter(str.isdigit, f))))
dict_model = torch.load('%s/%s' % (ckpt_dir, ckpt_lst[-1]))
net.load_state_dict(dict_model['net'])
optim.load_state_dict(dict_model['optim'])
epoch = int(ckpt_lst[-1].split('epoch')[1].split('.pth')[0])
return net, optim, epoch
Train
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
os.environ['PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF'] = 'max_split_size_mb:128'
dir_img = 'C:/Users/pinb/Desktop/imgs'
dir_mask = 'C:/Users/pinb/Desktop/masks'
transform = transforms.Compose([Normalization(mean=0.5, std=0.5), RandomFlip(), Rotate(angle_range=(-90, 90)), ToTensor()])
train_set, val_set, test_set = create_datasets(img_dir=dir_img, mask_dir=dir_mask, transform=transform)
# 훈련 파라미터 설정하기
lr = 1e-3
batch_size = 4
num_epoch = 10
base_dir = './2nd_Battery/unet'
ckpt_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, "checkpoint")
log_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, "log")
# 네트워크 생성하기
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
net = UNet().to(device)
# 손실함수 정의하기
fn_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss().to(device)
# Optimizer 설정하기
optim = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
# 그 밖에 부수적인 functions 설정하기
fn_tonumpy = lambda x: x.to('cpu').detach().numpy().transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
fn_denorm = lambda x, mean, std: (x * std) + mean
fn_class = lambda x: 1.0 * (x > 0.5)
# 훈련을 위한 Transform과 DataLoader
loader_train = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
loader_val = DataLoader(val_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)
# 그밖에 부수적인 variables 설정하기
num_data_train = len(train_set)
num_data_val = len(val_set)
num_batch_train = np.ceil(num_data_train / batch_size)
num_batch_val = np.ceil(num_data_val / batch_size)
# Tensorboard 를 사용하기 위한 SummaryWriter 설정
writer_train = SummaryWriter(log_dir=os.path.join(log_dir, 'train'))
writer_val = SummaryWriter(log_dir=os.path.join(log_dir, 'val'))
# 네트워크 학습시키기
st_epoch = 0
# 학습한 모델이 있을 경우 모델 로드하기
net, optim, st_epoch = load(ckpt_dir=ckpt_dir, net=net, optim=optim)
for epoch in range(st_epoch + 1, num_epoch + 1):
net.train()
loss_arr = []
for batch, data in enumerate(loader_train, 1):
# forward pass
label = data['label'].to(device)
input = data['input'].to(device)
output = net(input)
# backward pass
optim.zero_grad()
loss = fn_loss(output, label)
loss.backward()
optim.step()
# 손실함수 계산
loss_arr += [loss.item()]
print("TRAIN: EPOCH %04d / %04d | BATCH %04d / %04d | LOSS %.4f" %
(epoch, num_epoch, batch, num_batch_train, np.mean(loss_arr)))
# Tensorboard 저장하기
label = fn_tonumpy(label)
input = fn_tonumpy(fn_denorm(input, mean=0.5, std=0.5))
output = fn_tonumpy(fn_class(output))
writer_train.add_image('label', label, num_batch_train * (epoch - 1) + batch, dataformats='NHWC')
writer_train.add_image('input', input, num_batch_train * (epoch - 1) + batch, dataformats='NHWC')
writer_train.add_image('output', output, num_batch_train * (epoch - 1) + batch, dataformats='NHWC')
writer_train.add_scalar('loss', np.mean(loss_arr), epoch)
with torch.no_grad():
net.eval()
loss_arr = []
for batch, data in enumerate(loader_val, 1):
# forward pass
label = data['label'].to(device)
input = data['input'].to(device)
output = net(input)
# 손실함수 계산하기
loss = fn_loss(output, label)
loss_arr += [loss.item()]
print("VALID: EPOCH %04d / %04d | BATCH %04d / %04d | LOSS %.4f" %
(epoch, num_epoch, batch, num_batch_val, np.mean(loss_arr)))
# Tensorboard 저장하기
label = fn_tonumpy(label)
input = fn_tonumpy(fn_denorm(input, mean=0.5, std=0.5))
output = fn_tonumpy(fn_class(output))
writer_val.add_image('label', label, num_batch_val * (epoch - 1) + batch, dataformats='NHWC')
writer_val.add_image('input', input, num_batch_val * (epoch - 1) + batch, dataformats='NHWC')
writer_val.add_image('output', output, num_batch_val * (epoch - 1) + batch, dataformats='NHWC')
writer_val.add_scalar('loss', np.mean(loss_arr), epoch)
# epoch 5마다 모델 저장하기
if epoch % 1 == 0:
save(ckpt_dir=ckpt_dir, net=net, optim=optim, epoch=epoch)
writer_train.close()
writer_val.close()
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0001 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0056
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0002 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0059
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0003 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0068
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0004 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0067
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0005 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0066
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0006 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0135
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0007 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0124
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0008 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0117
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0009 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0111
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0010 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0188
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0011 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0176
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0012 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0167
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0013 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0160
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0014 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0153
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0015 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0149
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0016 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0146
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0017 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0141
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0018 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0137
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0019 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0134
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0020 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0131
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0021 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0131
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0022 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0128
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0023 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0127
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0024 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0125
TRAIN: EPOCH 0006 / 0020 | BATCH 0025 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0122
...
TRAIN: EPOCH 0010 / 0020 | BATCH 0087 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0074
TRAIN: EPOCH 0010 / 0020 | BATCH 0088 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0073
TRAIN: EPOCH 0010 / 0020 | BATCH 0089 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0073
TRAIN: EPOCH 0010 / 0020 | BATCH 0090 / 3410 | LOSS 0.0078
Test
print('train set: ' + str(len(train_set)))
print('val set: ' + str(len(val_set)))
print('test set: ' + str(len(test_set)))
print('total: ' + str(len(train_set)+ len(val_set)+ len(test_set)))
train set: 13638
val set: 3896
test set: 1949
total: 19483
loader_test = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)
# 그밖에 부수적인 variables 설정하기
num_data_test = len(test_set)
num_batch_test = np.ceil(num_data_test / batch_size)
# 결과 디렉토리 생성하기
result_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'result')
if not os.path.exists(result_dir):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(result_dir, 'png'))
os.makedirs(os.path.join(result_dir, 'numpy'))
net, optim, st_epoch = load(ckpt_dir=ckpt_dir, net=net, optim=optim)
with torch.no_grad():
net.eval()
loss_arr = []
for batch, data in enumerate(loader_test, 1):
# forward pass
label = data['label'].to(device)
input = data['input'].to(device)
output = net(input)
# 손실함수 계산하기
loss = fn_loss(output, label)
loss_arr += [loss.item()]
print("TEST: BATCH %04d / %04d | LOSS %.4f" %
(batch, num_batch_test, np.mean(loss_arr)))
# Tensorboard 저장하기
label = fn_tonumpy(label)
input = fn_tonumpy(fn_denorm(input, mean=0.5, std=0.5))
output = fn_tonumpy(fn_class(output))
# 테스트 결과 저장하기
for j in range(label.shape[0]):
id = num_batch_test * (batch - 1) + j
plt.imsave(os.path.join(result_dir, 'png', 'label_%04d.png' % id), label[j].squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.imsave(os.path.join(result_dir, 'png', 'input_%04d.png' % id), input[j].squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.imsave(os.path.join(result_dir, 'png', 'output_%04d.png' % id), output[j].squeeze(), cmap='gray')
np.save(os.path.join(result_dir, 'numpy', 'label_%04d.npy' % id), label[j].squeeze())
np.save(os.path.join(result_dir, 'numpy', 'input_%04d.npy' % id), input[j].squeeze())
np.save(os.path.join(result_dir, 'numpy', 'output_%04d.npy' % id), output[j].squeeze())
print("AVERAGE TEST: BATCH %04d / %04d | LOSS %.4f" %
(batch, num_batch_test, np.mean(loss_arr)))
TEST: BATCH 0001 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0084
TEST: BATCH 0002 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0077
TEST: BATCH 0003 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0105
TEST: BATCH 0004 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0095
TEST: BATCH 0005 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0094
TEST: BATCH 0006 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0093
TEST: BATCH 0007 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0092
TEST: BATCH 0008 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0094
TEST: BATCH 0009 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0094
TEST: BATCH 0010 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0127
TEST: BATCH 0011 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0126
TEST: BATCH 0012 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0124
TEST: BATCH 0013 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0123
TEST: BATCH 0014 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0121
TEST: BATCH 0015 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0118
TEST: BATCH 0016 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0116
TEST: BATCH 0017 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0114
TEST: BATCH 0018 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0114
TEST: BATCH 0019 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0113
TEST: BATCH 0020 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0111
TEST: BATCH 0021 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0110
TEST: BATCH 0022 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0108
TEST: BATCH 0023 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0106
TEST: BATCH 0024 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0107
TEST: BATCH 0025 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0106
...
TEST: BATCH 0486 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0109
TEST: BATCH 0487 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0109
TEST: BATCH 0488 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0109
AVERAGE TEST: BATCH 0488 / 0488 | LOSS 0.0109
Result
##
lst_data = os.listdir(os.path.join(result_dir, 'numpy'))
lst_label = [f for f in lst_data if f.startswith('label')]
lst_input = [f for f in lst_data if f.startswith('input')]
lst_output = [f for f in lst_data if f.startswith('output')]
lst_label.sort()
lst_input.sort()
lst_output.sort()
##
id = 0
label = np.load(os.path.join(result_dir,"numpy", lst_label[id]))
input = np.load(os.path.join(result_dir,"numpy", lst_input[id]))
output = np.load(os.path.join(result_dir,"numpy", lst_output[id]))
## 플롯 그리기
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(input, cmap='gray')
plt.title('input')
plt.subplot(132)
plt.imshow(label, cmap='gray')
plt.title('label')
plt.subplot(133)
plt.imshow(output, cmap='gray')
plt.title('output')
plt.show()
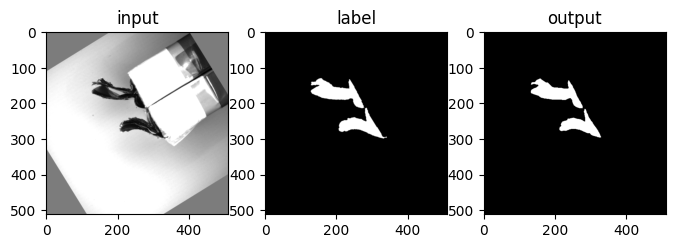
결과
Result
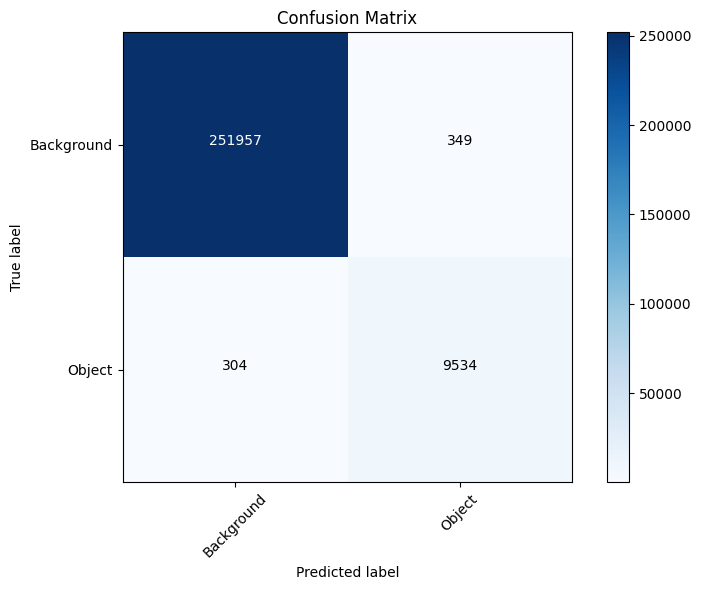
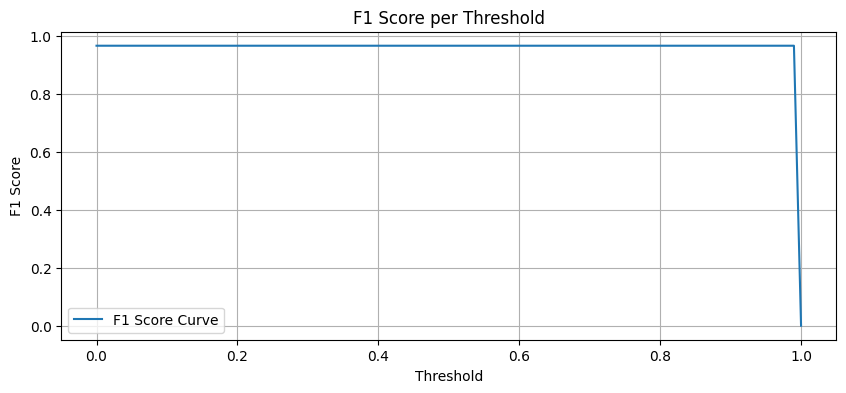
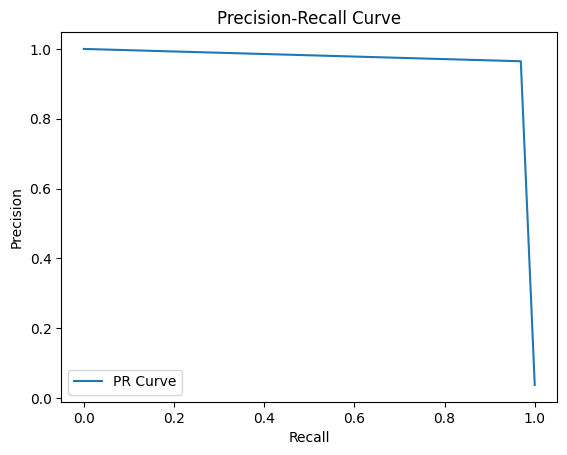
참고¶
- 지능화파일럿 과목, 윤성철 교수
- ChatGPT
- DACON-UNET